Valve is a gas distribution mechanism to cam start the whole chain of movement in the end parts, is an important component of the car, its design must be considered from the whole gas distribution structure, to avoid excessive impact and vibration due to the valve fall seat to withstand, thus causing the valve and valve seat wear. Therefore, the production of valve materials should have sufficient strength, toughness and surface hardness, under this premise, the valve should be light, the structure should be simple, easy to process, the neck shape is appropriate, in order to reduce the resistance to gas flow, increase the intake charge; at the same time, the design of the valve and the design of the cylinder head to be closely coordinated, the valve seat must be strengthened around the cooling, the temperature as far as possible, if the structure permits, it should be maximized to increase the length of the tube, and the valve seat should have sufficient strength, toughness and surface hardness. Appropriately reduce the valve lift and tube clearance to reduce the valve temperature.
Valve mainly consists of disk outer circle, cone angle, disk thickness, neck, rod and locking clip groove and other parts.
Valve disk outer circle
In order to obtain the best volumetric efficiency, the head diameter in the valve design is usually the larger the better, but due to the limitations between the combustion chamber, the intake valve diameter for the cylinder diameter of 42 ~ 48%. Generally, considering the suction effect, the intake valve diameter should be 15~20% larger than the exhaust valve to improve the filling efficiency.
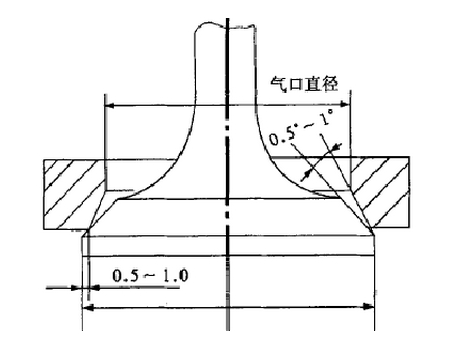
Valve cone angle
The sealing cone of the valve head has two types: 30° and 45°. The larger cone angle can improve the rigidity of the edge of the valve head and ensure good auto-centering of the valve cone and the base and a larger specific pressure of the sealing surface, which is conducive to the milling of carbon deposits. Most valve designs use 45° taper angle, 45° taper angle can not only provide good sealing, but also to meet the wear resistance requirements of valve seating.
Valve Disk thickness
In order to ensure that the valve head has sufficient rigidity and is as light as possible, the disk thickness dimensions should be selected reasonably in the design.
Valve Neck
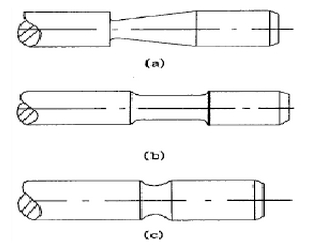
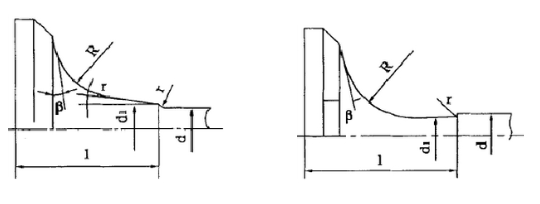
Neck transition cone angle and transition radius of the size of the airflow has a great impact on the cone angle should ensure that the airflow of the smooth transition, but more importantly, to ensure that the valve neck surface of the stress distribution is uniform. Generally speaking, the transition cone angle and transition radius of the exhaust valve are larger than that of the intake valve. In addition, under the action of uniform pressure, the deformation of the valve head mainly occurs at the outer edge of the disk, in the case of a certain disk thickness, the rigidity of the valve head mainly depends on the size of the transition cone angle and transition radius.
Valve stem Diameter
Valve stem diameter is mainly determined according to the durability requirements of the exhaust valve, in order to facilitate the processing of the cylinder head, the diameter of the intake and exhaust valve conduit is generally the same, the intake and exhaust valves also usually use the same nominal size of the rod, in the actual design of the valve diameter is generally selected according to the φ7 ~ φ12. Commonly used valve stem and tube fit clearance: intake valve for 0.04 ~ 0.08mm, exhaust valve for 0.05 ~ 0.09mm, due to the gap between the valve and tube will affect the valve strength at the valve stem and valve head smooth transition, so the minimum gap should be selected so that there is no danger of the valve stem stuck in the tube, so that the highest operating temperature, but also be able to retain the lubricant film to avoid consequent scuffing and wear of the valve stem section.
Valve Clamping grooves
Valve locking grooves can be designed with three types of grooves: conical grooves, square grooves and circular grooves. Among them, the circular groove can be divided into single, double and multi-channel circular groove, single circular groove structure can be applied to virtually any rod diameter of the valve, the main advantage of this design compared with the conical groove and square groove is that the circular groove reduces the notch sensitivity; double groove of the circular surface has a lower notch sensitivity, and the two grooves can produce additional shear force; multi-channel groove (3-4) design form in addition to the advantages of the double circular groove, but also to facilitate the assembly of the locking clip and locking clip groove against each other, not just for the assembly of the locking clip and locking clip slot. In addition to the advantages of the groove, but also to facilitate in the assembly of the locking clip and the locking clip groove against each other, not only for clamping the valve stem, this locking clip device rely on the groove and the locking clip concave, convex edge of the contact surface between the abrasion resistance requirements. For some models, sometimes in the valve stem near the locking clip groove to car out a ring groove, the installation of spring retaining ring, when the valve stem from the locking clip groove breakage, the ring is blocked by the valve guide, the valve from falling into the cylinder. The position of the ring groove should be able to ensure that the fall of the valve is only 1~2mm greater than the maximum lift of the valve.